Due to the large number of alkaline water devices on the market, the question “how to recognise a real water ioniser?” has become increasingly important for users. Although every system that produces alkaline water is called an ioniser, a real water ioniser must have certain technical equipment and measurable performance values. Ionisation is not only possible by raising the pH level of the water, but also by separating it into its ions through electrolysis technology.
The internal structure of the device, the materials used, the electrical capacity and the long-term operating stability play a decisive role here. In order to distinguish a real water ioniser, it is necessary to focus on the technical details and evaluate the features offered by the device based on scientific criteria. The seven technical criteria discussed in this context provide a basic roadmap to understand whether a device really ionises or not.
What is a Water Ioniser?
In recent years, with the increasing expectation that water is not only clean but also has functional properties, the question of “what is a water ioniser?” has become more popular. Water ionisers are devices that separate the natural minerals in water into positive and negative ions by subjecting the water passing through it to electrolysis. During this process, the electrical charge balance of the water changes and the pH value can be increased in a controlled manner to obtain alkaline water or acidic water by lowering it. Thus, water production suitable for different purposes is provided through a single device.
The ionisation process is not only limited to pH change. The oxidation-reduction potential and mineral distribution of water are also affected by this process. This transformation, which takes place thanks to the electrolysis plates, helps the water to gain a more active form in its molecular structure. In this respect, water ionisers differ from conventional filter systems that only aim to reduce contaminants in water and offer an advanced technology that aims to transform the structural properties of water.
While a conventional water purifier usually focuses on removing sediment, chlorine and similar undesirable substances from water, water ionisers go beyond the filtering stage and aim to give water functional properties. Thanks to the ionised water device features, pre-filtration systems and ionisation technology work together. Water ionisers are considered as a holistic solution that not only cleans the water but also restructures it according to its intended use.
7 Technical Criteria that Define a True Water Ioniser
The technical infrastructure of the device contains criteria that allow you to understand real water ionisation. For ionisation to be truly effective, certain criteria must be met precisely. These criteria mean that the device not only alkalises the water, but also ensures a stable and controlled ionisation.
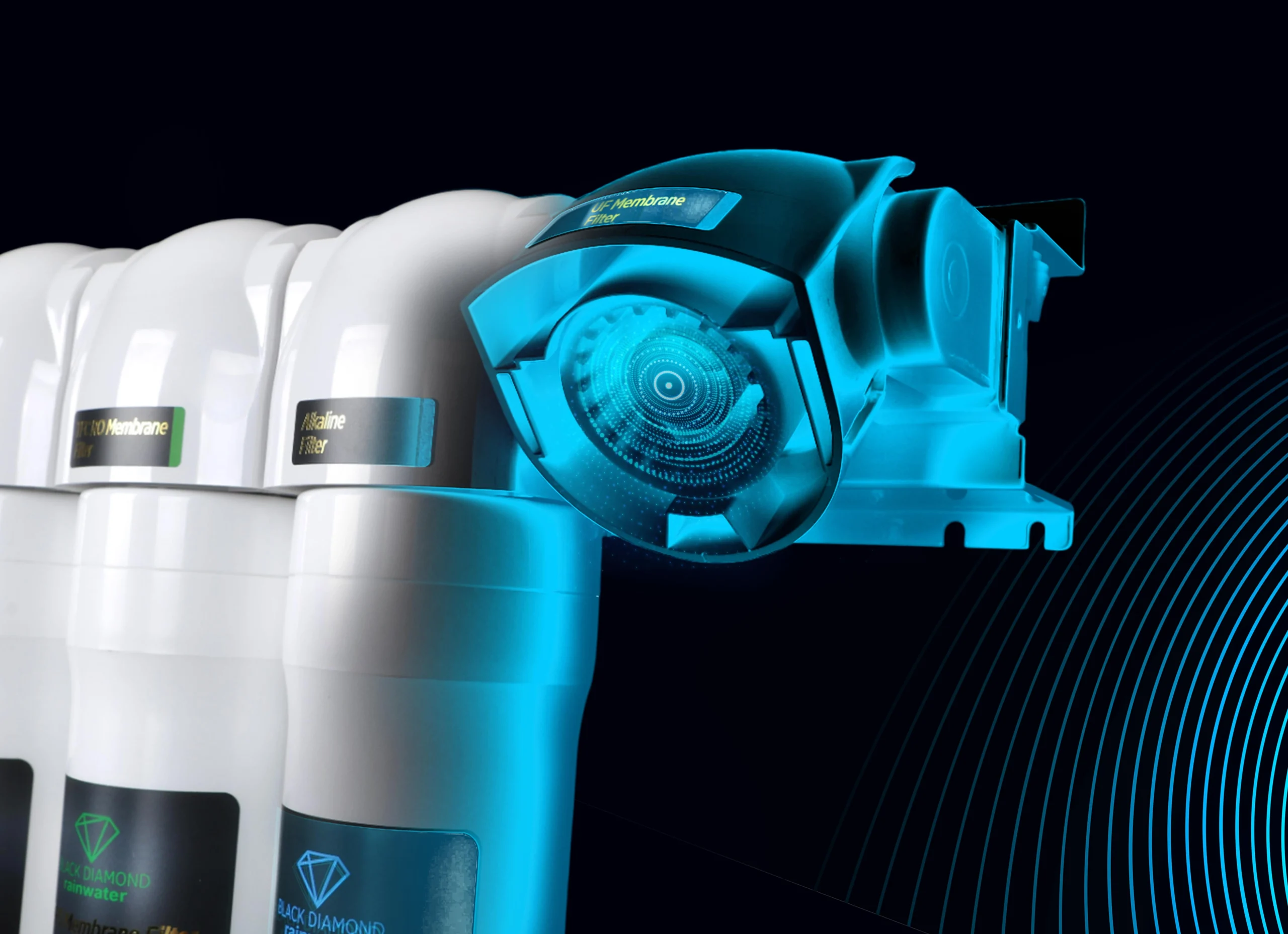
Criterion 1: Presence and Characteristics of Electrolysis Plates
The basis of real ionisation is electrolysis plates. These plates ensure that the minerals in the water are separated by electric current and directly influence the quality of the ionisation. The number of plates, the surface area and the material used are decisive for the stability of the resulting water.
Criterion 2: Platinum Plating Quality
The platinum plating quality of the electrolysis plates plays a critical role in the performance and durability of the device. High purity platinum plating both improves ionisation efficiency and minimises wear in long-term use.
Criterion 3: Power Supply and Voltage Capacity
In order for the ionisation process to take place properly, the device must have a strong and balanced voltage capacity. Insufficient power may cause incomplete ion separation and the expected water properties may not occur.
Criterion 4: pH Adjustment Capability (Multilevel)
The question “What is pH?” is fundamental to understanding ionised water technology. A true ioniser has the ability to produce water at different pH levels and offers the user multi-level adjustment. In this way, the pH value can be determined in a controlled manner according to the intended use of the water.
Criterion 5: Ability to Generate ORP Value
One of the important indicators of ionisation is the ORP value. The ability to produce low ORP indicates that the electrolysis performance of the device is strong and that the water acquires reducing properties.
Criterion 6: Continuous and Stable Performance
In order for a water ioniser to be considered truly high-quality, it must maintain its performance over time. Devices that can maintain the ionisation quality of the first day in the long term are considered technically reliable.
Criterion 7: Ability to produce acidic water
The production of acidic water is a natural consequence of the ionisation process and shows that the device can work in both directions. This offers alternatives not only for drinking water, but also for cleaning and hygiene use.
Simple Alkaline Water Difference with Real Ioniser
Not every alkaline water producing device on the market is considered a true ioniser. While simple alkaline systems generally increase the pH of water through the properties of minerals after filtration, real ionisers change the structure of water with electrolysis technology. This difference has a direct impact on the stability and usage areas of the water obtained.
Ionisation Technology vs Filtration Technology
While filtration systems aim to remove unwanted substances from water, ionisation technology transforms the chemical properties of water. For example, a water purification filter reduces sediment and some harmful components in the water, while the ionisation process activates minerals in the water, resulting in water with different properties. These two technologies are often used complementary to each other.
How to Care for Water Ioniser?
Maintenance is of great importance for users who want to get long-term efficiency from the device and maintain the quality of the water produced. Since ionisers are sensitive systems operating with electrolysis technology, performance loss may occur without regular maintenance and the pH balance of the water may not be produced at the desired level. Therefore, the maintenance process includes not only the clean appearance of the device, but also the healthy continuation of its technical functions.
One of the most important stages of maintenance is to clean the electrolysis plates from lime and mineral deposits. Over time, minerals in the water can accumulate on the plate surfaces and reduce the electrolysis efficiency. This leads to a decrease in the ionisation power and the water does not gain stable properties. Regular plate cleaning in accordance with the cleaning programmes recommended by the manufacturer supports the device to operate close to its first day performance.
Checking and timely replacement of the internal filters is also an integral part of the maintenance process. Filters allow the water to pass through pre-treatment before entering the ionisation unit and protect the electrolysis system. Failure to replace expired filters may both adversely affect the water quality and accelerate the formation of sediment and lime scale in the internal parts of the device. For this reason, filter change periods should not be neglected.
Internal cleaning and general control of the device constitute the complementary steps of maintenance. Protecting the hose connections, water inlet and outlet points and electronic components from moisture is important for the safe operation of the device. In addition, considering the effects of some substances such as fluoride in water on the system over time, maintenance intervals should be planned according to the conditions of use. Regular and conscious water ioniser maintenance both prolongs the life of the device and protects the quality of the water produced for a long time.
What are the Health Benefits of Ionised Water?
The health effects of ionised water are associated with the active ingredients it contains. Especially the question “what are the benefits of hydrogenated water?” has increased the interest in this field in recent years. When the balanced pH structure of the water obtained in the ionisation process is evaluated together with the subject of “what is water softening?“, the ease of drinking water and its role in daily consumption can be understood more clearly. All these effects gain meaning when supported by conscious use and correct device selection.

 TR
TR
 Blog
Blog