Hydrogenated water, which has become prominent among functional beverages in recent years, is the subject of scientific studies due to its interaction with free radicals at the cellular level. Especially the antioxidant effects of hydrogenated water are evaluated in a clearer framework with the understanding of oxidative stress-related processes. In this context, hydrogenated water is considered as a supportive element in addition to classical nutritional approaches.
What is Oxidative Stress and Why is it Important?
Oxidative stress is a biochemical condition that occurs as a result of the disruption of the balance between free radical production and antioxidant defence mechanisms in the body. This imbalance may adversely affect the structural integrity and function of cells. The uncontrolled increase in free radicals can lead to lipid peroxidation in cell membranes, structural deterioration of proteins and DNA damage and accelerate cellular aging processes. Long-term persistence of oxidative stress may lead to weakening of the immune system and increase in inflammatory processes.
This is associated with the development of cardiovascular diseases, metabolic disorders and some chronic diseases. Therefore, controlling oxidative stress is critical for maintaining cellular health and maintaining general physiological balance.
Free Radicals and Oxidative Damage
Free radicals are reactive molecules that occur naturally during metabolic activities but can damage cell membranes, proteins and DNA when uncontrolled. Accumulation of these molecules can accelerate the cellular aging process by triggering oxidative damage.
Effects of Oxidative Stress on Health
Long-term oxidative stress is associated with many health problems such as chronic inflammation, cardiovascular disease and kidney disease. Therefore, maintaining oxidative balance is critical for overall health.
Importance of Antioxidant Defence System
The human body continuously produces free radicals as a result of metabolic activities, environmental factors, stress and dietary habits. These reactive molecules have the potential to damage cell membranes, proteins and DNA structure. To counterbalance these harmful effects, the body develops a comprehensive protection network consisting of enzymatic defence mechanisms such as superoxide dismutase, catalase and glutathione peroxidase as well as non-enzymatic antioxidant systems such as vitamin C, vitamin E and polyphenols.
The main task of the antioxidant defence system is to maintain healthy cellular functions by maintaining oxidative balance. However, the effectiveness of these systems may decrease in conditions such as aging, chronic diseases, intense oxidative stress and malnutrition. In such a situation, the body’s own defence capacity may be insufficient and external supportive approaches may be needed.
At this point, hydrogen water stands out with its antioxidant potential. While targeting harmful free radicals thanks to its selective mechanism of action, it draws attention by assuming a supportive role without disturbing the physiological balance. Such support should be considered as a complementary element rather than replacing the basic defence systems.
Difference Between Normal Water and Hydrogenated Water
While normal water consumed in daily life meets the basic hydration needs, hydrogenated water, which has come to the fore in recent years, is considered in a different position with its content of dissolved molecular hydrogen. The difference between these two types of water is not limited to the drinking experience; it is also evaluated in terms of antioxidant potential, cellular interaction and physiological support.
- While normal water mainly provides hydration, hydrogenated water contains molecular hydrogen.
- The antioxidant capacity of hydrogenated water is due to the dissolved hydrogen gas.
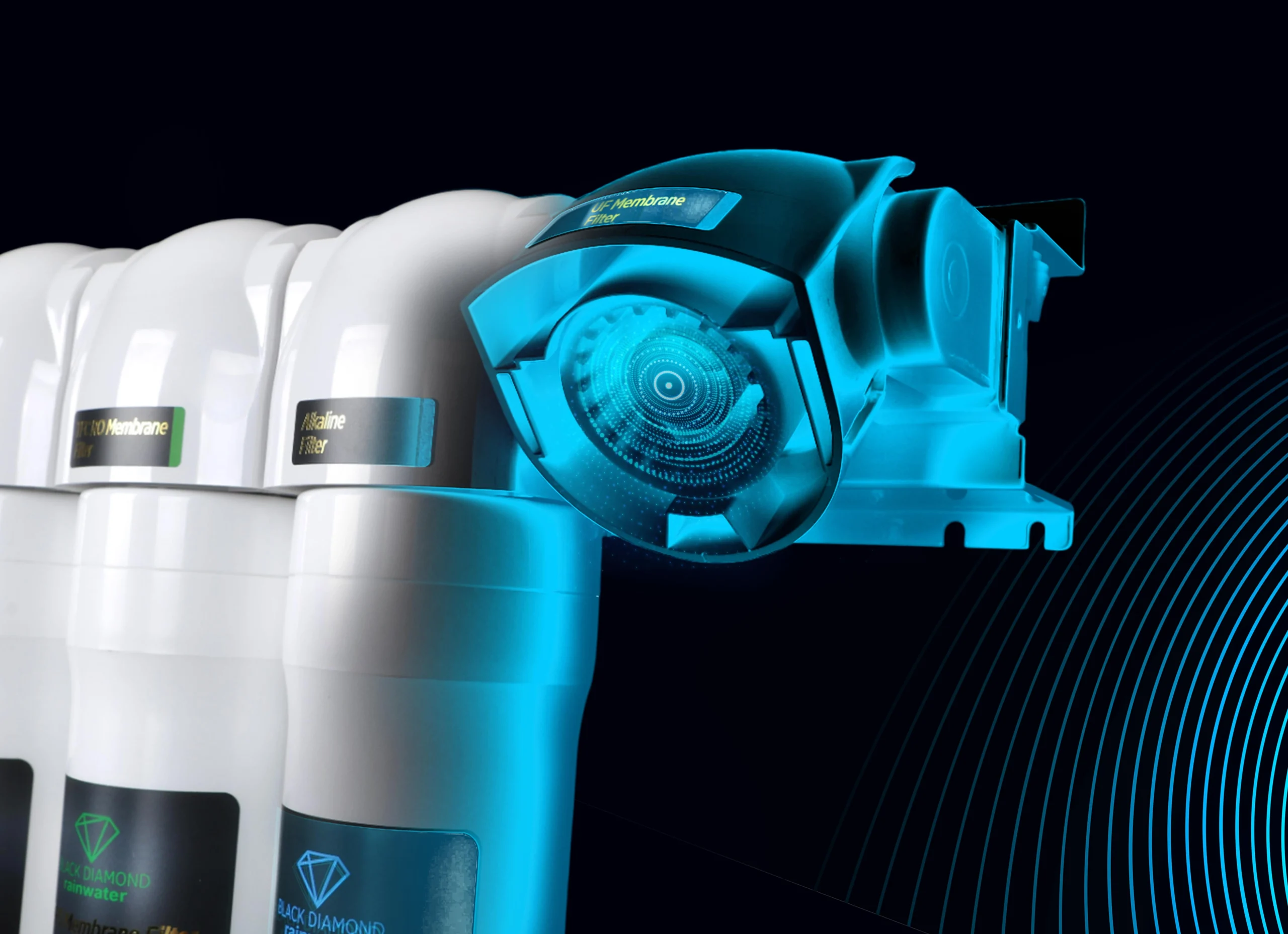
- Hydrogen water is obtained with a special hydrogen water purifier.
- While normal water has no antioxidant effect, hydrogenated water can interact with oxidative stress.
Since the effects on health vary depending on individual needs and continuity of use, both types of water gain meaning when they are handled within the framework of a conscious and balanced approach.
Antioxidant Mechanism of Hydrogenated Water
It is based on molecular hydrogen penetrating into the cell and interacting with harmful free radicals. The antioxidant mechanism of hydrogenated water benefits offers a selective and cell-friendly effect model unlike classical antioxidants.
Selective Antioxidant Feature
Molecular hydrogen targets only the most harmful free radicals and does not interfere with beneficial oxidative signalling molecules. This selectivity contributes to the maintenance of cellular communication and metabolic balance.
Mechanism of Action at Cellular Level
The very small structure of the hydrogen molecule makes it possible to easily cross cell membranes. In this way, it can assume a protective role by reaching the areas where oxidative damage is intense in the cell.
ORP (Oxidation-Reduction Potential) and Antioxidant Capacity
The ORP value indicates the oxidising or reducing capacity of a liquid. Hydrogenated water usually has a negative ORP value and this reflects its antioxidant potential. This effect can be interpreted more accurately by evaluating the pH value of the water.
How Long Does the Antioxidant Effect of Hydrogenated Water Last?
The antioxidant effect of hydrogenated water is known to start within a short time after consumption. Since the structure of molecular hydrogen is extremely small and neutral, it can quickly pass through cell membranes, mitochondria and even the blood-brain barrier. This results in the antioxidant effect usually occurring within minutes to a few hours. However, this rapid effect also has a transient characteristic.
Molecular hydrogen is not stored in the body and is quickly removed through respiration or the circulatory system as a result of metabolic processes. Therefore, the antioxidant support provided by hydrogenated water is limited to one-time consumption. The continuity of the effect is associated with regular and conscious consumption. Intermittent or irregular use is not expected to provide permanent antioxidant protection at the cellular level.
At this point, the effect of hydrogenated water should be evaluated together with general fluid intake and hydration status of the body. Adequate water consumption is a fundamental factor in supporting circulation, removing metabolic wastes and maintaining intracellular balance. Therefore, when the antioxidant contribution of hydrogenated water is considered within the scope of the question “what are the benefits of drinking water to the body?“, it gains meaning as an element that complements healthy living habits rather than a miraculous effect alone.
Can Hydrogenated Water Be Used Instead of Regular Antioxidant Supplements?
Hydrogenated water should not be considered as a direct replacement for conventional antioxidant supplements. Antioxidants taken through nutrients such as vitamin C, vitamin E, polyphenols and minerals or in the form of supplements play unique and indispensable roles in many biological processes such as the immune system, hormone synthesis, enzyme activity and cell renewal. Unlike these substances, hydrogenated water is not a nutrient, but a supportive element that interacts with free radicals in the cellular environment.
The antioxidant effect of hydrogenated water is due to the selective nature of molecular hydrogen and this effect is usually short-lived. Hydrogen, which is not stored in the body, requires regular consumption and due to this feature, it cannot replace the permanent biological building blocks provided by antioxidants taken through nutrition. Therefore, hydrogen water should be considered as a complement to a balanced diet and antioxidant supplements, not as an alternative.
In this respect, the general quality of water also gains importance. For example, the question “what is an activated carbon filter and what does it do?” defines filtration systems that improve the taste and drinking quality of water by retaining chlorine, heavy odours and organic compounds in water and forms the basis of healthy water consumption. Similarly, the statement “what is hard water and what are the characteristics of hard water?” describes the chemical structure of waters with high calcium and magnesium content and the effects of these waters on both taste and usage characteristics.
Hydrogen water can be considered as a supportive element for healthy living and antioxidant balance, but it should not be expected to replace medical or nutritional antioxidant sources. The best approach is to position hydrogen water in a holistic health approach together with adequate and balanced nutrition, quality water consumption and supplements used under expert control when necessary.

 TR
TR
 Blog
Blog